Teaching Subitizing
Number Sense
Wondering how to get started Teaching Subitizing? You’re in the right place!
Subitizing, or subitising, sounds complicated, but this early years numeracy concept is surprisingly straightforward and FUN to teach.
In this post, you will find our top tips for teaching subitizing to young children in preschool, pre-k, or kindergarten classrooms. You’ll also find a handy library of theme and basic subitizing teaching resources to help you teach subitizing skills like a BOSS!
What is Subitizing and Number Sense?
The word Subitize originates from the Latin word meaning suddenly. So teaching children to subitize means you are teaching them to “suddenly recognise how many in a collection without counting.” Or see how many at a glance.
Being able to subitize or instantly recognize “how many” in a small set, without counting, is an important early years numeracy skill that is the foundation of many other math concepts. This early years math skill helps children to build number sense and flexibility about the essential properties of numbers, contributing significantly to their early math skills.
When you teach kids to subitize they will learn to think of a collection in component parts which will help them in the future to see that:
- Making tidy arrangements makes it easier to see how many there are in collections – (Counting Strategies)
- Any collection can be separated into parts and each part can be represented by a number ” Thinking – part-part-whole can help us see “how many” in total (Part-Part-Whole Computational Thinking)
- The same number can be thought of in parts in many different ways (Partitioning Strategy)
- A number can be thought of in more than two parts
Subitizing can be further divided into perceptual subitizing, used for smaller numbers, and a more advanced form called conceptual subitizing. Conceptual subitizing refers to the ability to recognize larger numbers by grouping them into recognizable patterns, rather than counting each item individually. For example, familiar arrangements such as tally marks allow for quicker recognition of totals.
(First Steps in Mathematics 2008).
Types of Subitizing
The subitizing concept consists of 2 levels of developmental components; conceptual and perceptual subitizing.
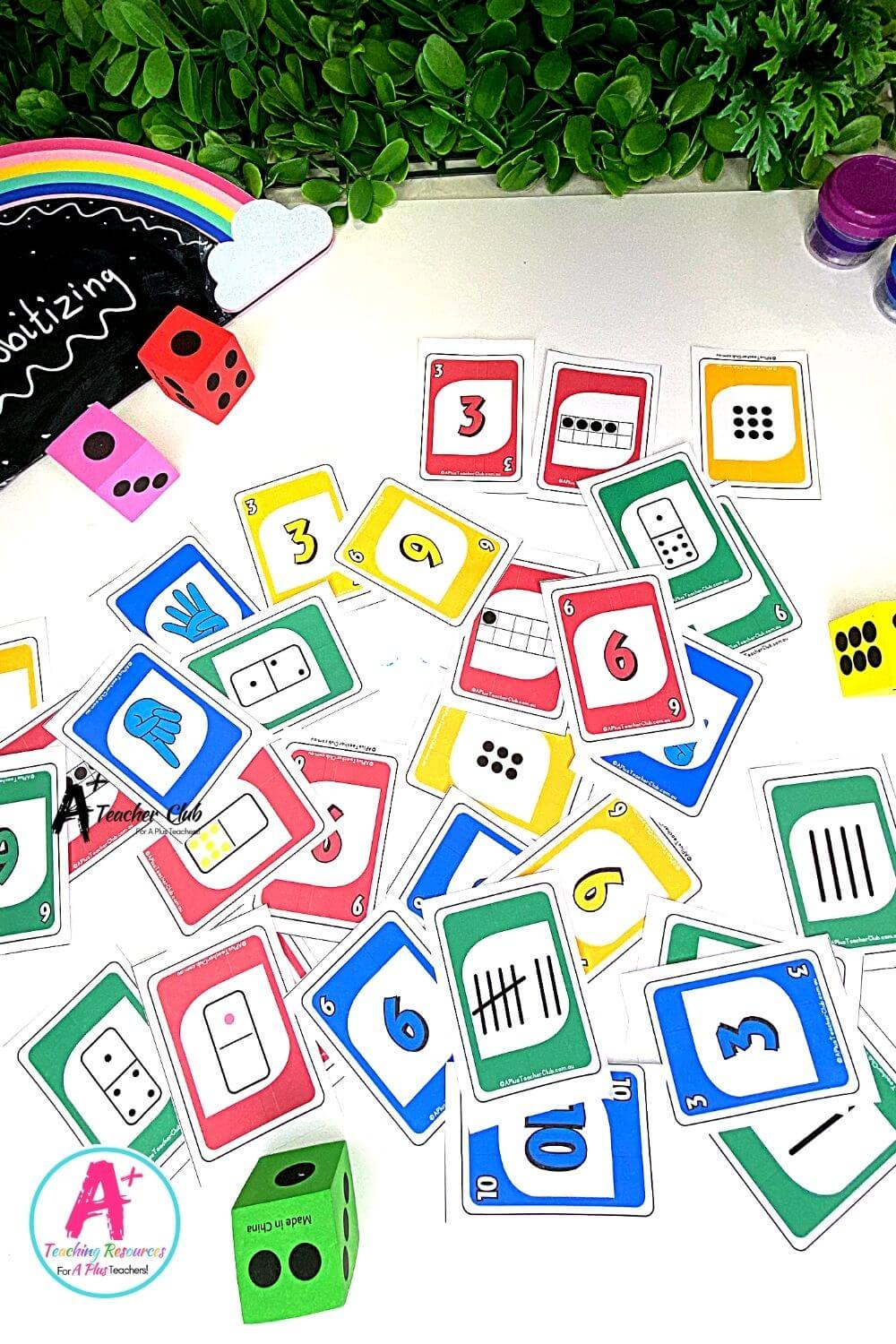
- Perceptual subitizing is the ability to instantly recognise how many are in a small set, usually up to 4, 5 or 6 and usually in standard dot dice formations
- Conceptual subitizing is recognising smaller groups within a larger set and adding or combining those small groups together, such as two dots plus two dots equals four dots, or three dots and three dots makes six dots. This is usually taught using non-standard dot formations.
Why Teach Subitizing?
Teaching subitizing is essential for building a strong foundation in math skills, particularly in the primary grades. When students learn to subitize, they develop a robust number sense, which is the ability to understand the relationships between numbers and quantities. This foundational skill is crucial as it underpins more complex mathematical concepts such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
By teaching subitizing, educators can help students build a deeper understanding of these mathematical concepts. For instance, when students can instantly recognize that two dots plus two dots equals four dots, they are engaging in early addition without even realizing it. This ability to see and understand quantities at a glance enhances their problem-solving skills, as they learn to recognize patterns and relationships between numbers.
Moreover, subitizing helps students develop critical thinking skills. In real-life situations, being able to quickly estimate quantities or make rapid calculations without counting can be incredibly useful. Whether it’s determining how many apples are in a basket or quickly assessing the number of people in a room, subitizing equips students with practical skills they will use throughout their lives. By incorporating subitizing into math lessons, educators can ensure that students develop a strong foundation in math skills that will benefit them throughout their academic careers.
Top Tips For Teaching Subitizing
Here are a few tips to effectively teach subitizing to young learners.
The key top tip for teaching subitizing is to teach students to see the patterns of the collections in the perceptual or standard groups first. As the brain can easily subitize collections up to 5 so this is where using dice comes in!
Once students have mastered subitising 1-5 in regular formations, extend this to include non-standard formations.
From the perceptual move them onto conceptual subitizing, that’s larger collections 6-12. To subitize larger amounts teach students how to see 2 or three smaller sets within the total collection.
A fun way to discourage students from counting the collections is to encourage your students to take a “snapshot” of the collection. Do this by showing a collection of objects for a few seconds and then invite the students to make a mental image of the set pattern or create a “snapshot”. This method will encourage students to improve their quick recognition skills.
Once students can do this deepen their understanding and number sense by teaching them to use subitising to order groups of objects as well as use subitising to compare collections.
In summary, the best subitizing teaching programs need to include teaching students perceptual subitizing first followed by conceptual subitizing, including teaching students to:
- Recognise the number of items in a small collection without counting
- Use subitising to order groups of objects
- Use subitising to compare collections
Teaching Subitizing Strategies
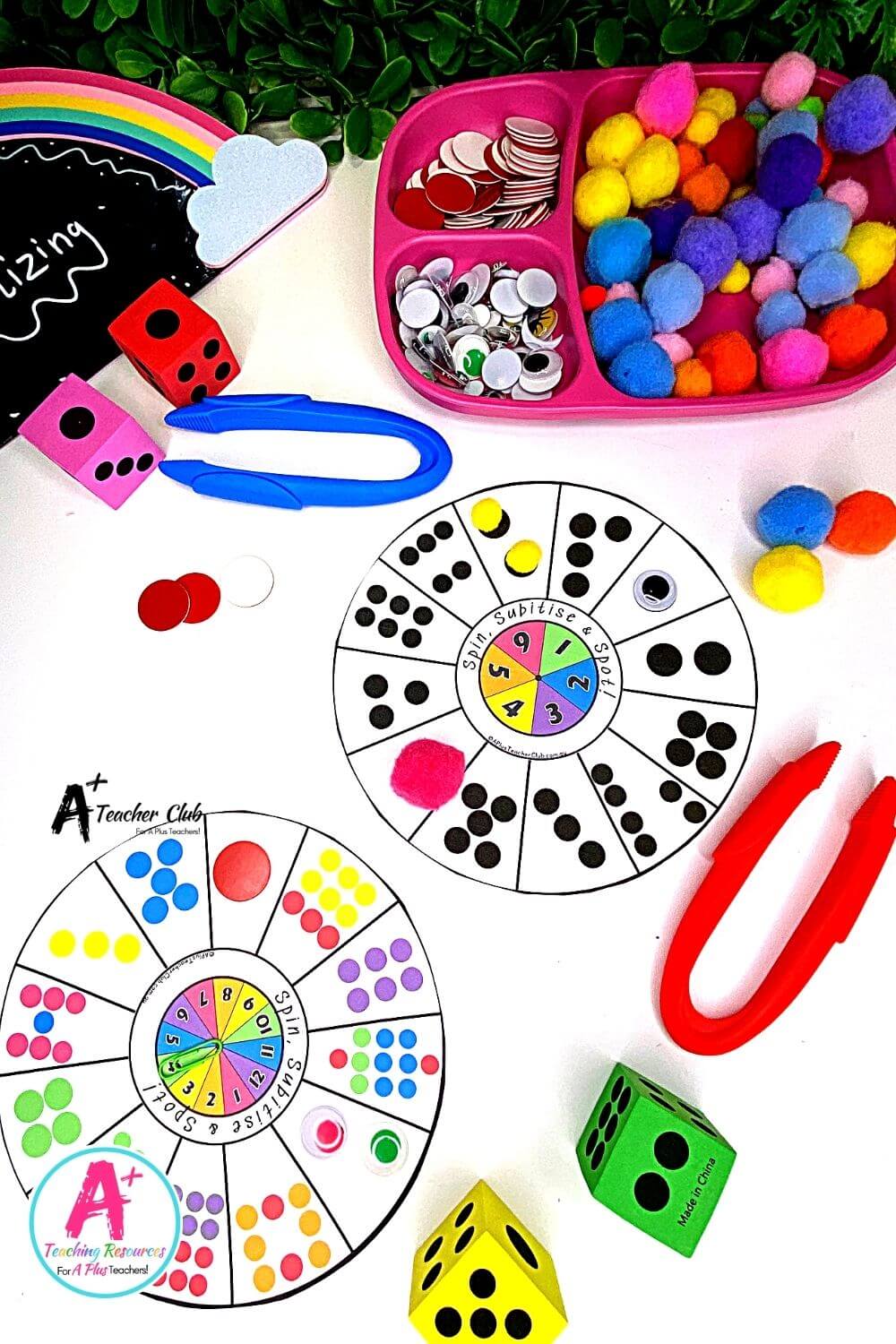
There are several effective strategies that educators can use to teach subitizing. One powerful approach is to use visual aids, such as ten frames or dot patterns. Ten frames, which consist of a grid with 10 squares, help students visualize quantities and see patterns. Dot patterns, often used in dice games, also help students recognize quantities quickly.
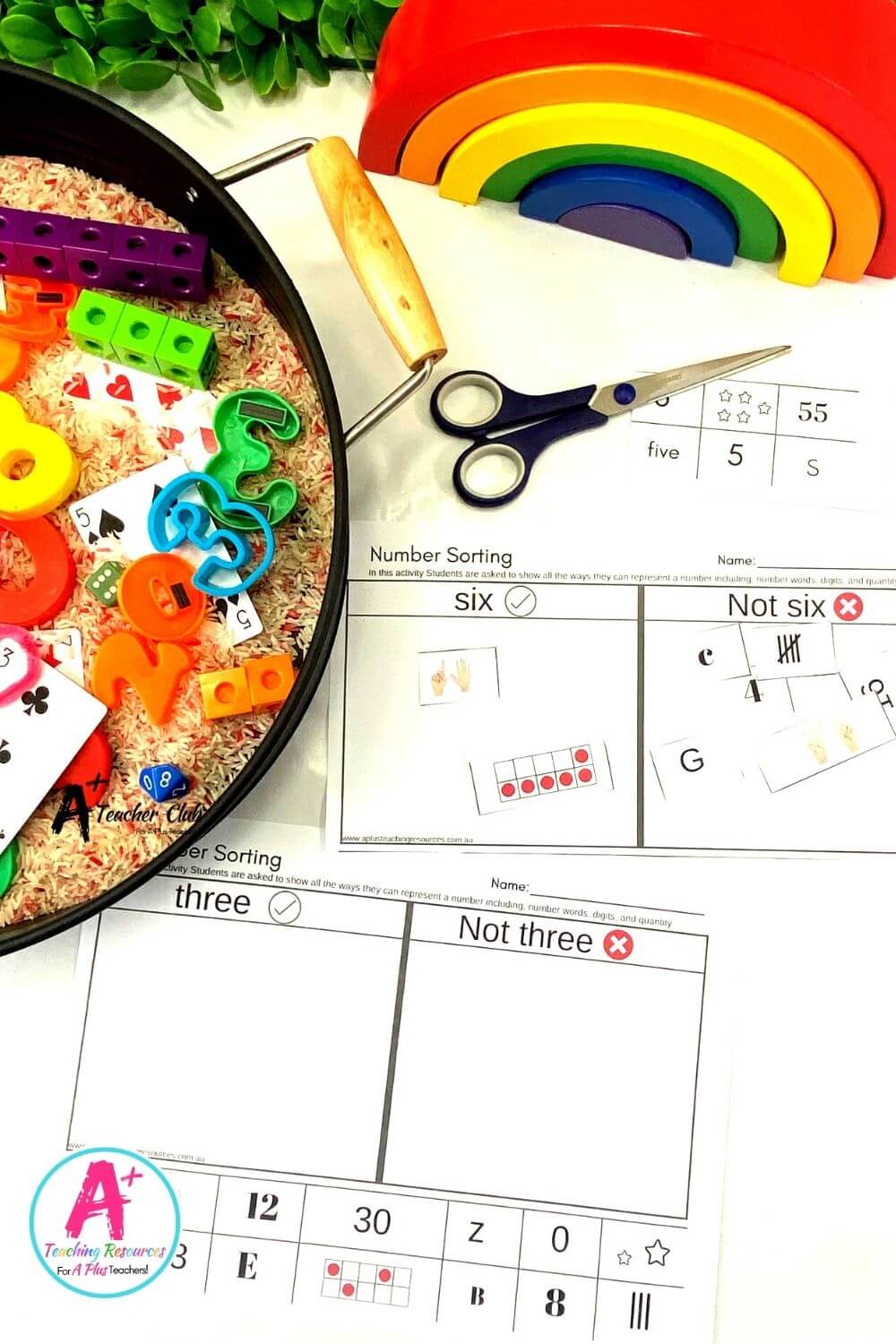
Games and activities are another engaging way to teach subitizing. Simple games like “How Many Fingers?” or “How Many Objects?” can make learning fun. In these games, students are shown a hand with a certain number of fingers raised or a set of objects and asked to identify the quantity. These activities not only make learning enjoyable but also reinforce subitizing skills.
Teaching subitizing in small groups can be particularly effective. Small group settings allow students to work together, share their thinking, and learn from each other. By encouraging students to explain their reasoning and justify their answers, educators can help them develop their problem-solving skills and build confidence in their mathematical abilities.
Technology can also be a valuable tool in teaching subitizing. Online games and apps that focus on recognizing quantities provide additional practice and support. These resources can be especially helpful for differentiating instruction and meeting the needs of diverse learners. By incorporating a variety of strategies, educators can effectively teach subitizing and help students develop strong math skills.
Subitizing Activities and Resources
There are many activities and resources available to teach subitizing, each designed to make learning this essential skill both fun and effective. Here are some of the best tools and activities to incorporate into your math lessons:
- Ten Frames: These visual aids consist of a grid with 10 squares and are excellent for helping students visualize quantities. By filling in the squares, students can easily see and recognize numbers up to ten.
- Dot Patterns: Using dot patterns, such as those found on dice, helps students quickly recognize quantities. These patterns are particularly useful for teaching perceptual subitizing.
- “How Many Fingers?” Game: In this game, students are shown a hand with a certain number of fingers raised and asked to identify the quantity. This simple yet effective game helps reinforce subitizing skills.
- “How Many Objects?” Game: Similar to the finger game, this activity involves showing students a set of objects and asking them to identify the quantity. It’s a great way to practice subitizing with different types of items.
- Tally Marks: Using tally marks is another effective visual aid. By grouping marks in sets of five, students can quickly see and count quantities without having to count each mark individually.
- Small Group Activities: Working in small groups allows students to collaborate and learn from each other. Activities that involve recognizing quantities and solving math problems together can be particularly beneficial.
By incorporating these activities and resources into your math lessons, you can help students develop their subitizing skills and build a strong foundation in math. Whether using ten frames, dot patterns, or engaging games, these tools will make learning subitizing an enjoyable and effective experience for your students.
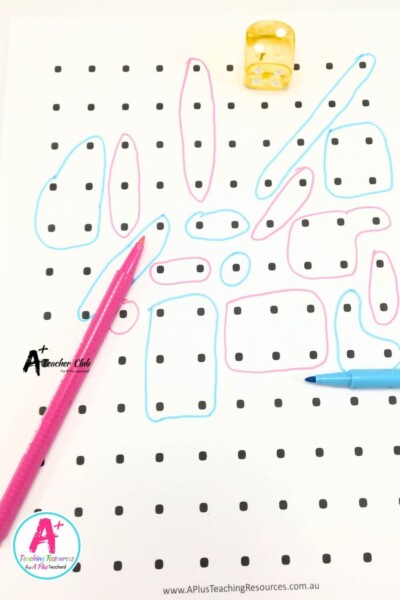
Below you will find our subitizing resources collections, there are games, flashcards, clip cards, playdough mats, assessment crafts, worksheets, and online games, there’s plenty to inspire you and your students. Enjoy! One engaging activity is using dot cards where students quickly identify how many dots they see on a card.
Resources listed in this collection
Click to jump to...Subitising Activities
More Subitising Activities

Subitising - Unicorn Theme

Subitising - Sunflower Seeds

Cutting Activities - Maths

Subitising PowerPoint Games

Subitising Activities

Subitising - Dino Theme

Online Perceptual Subitizing Games 1-6

Subitising 1-6 (ten frames)

Subitising 1-6 (dice & ten frames)

Subitising 1-6 Dots

Subitising 1-6 Dice
Can't find what you're looking for?
Send us a request! Use this form to request a resource. Please give details of the learning area, topic, year level, curriculum links. We’ll be happy to take a look to see if we can fit it in. Unfortunately a request does not guarantee we will be able to make it!
"*" indicates required fields